[컴퓨터 보안] Computer Security Overview
in CS Review on ComputerSecurity
컴퓨터 보안 복습
3학년 2학기에 수강하게 된 컴퓨터 보안이라는 과목에 대해 정리해보려 한다. 이 과목은 다른 과목에 비해 내 진로에 있어 중요성이 떨어질 수 있으나 그래도 열심히 정리해보려 한다.
Computer Security Overview
The CIA Triad(정보보안의 3대 요소) / Key Security Concepts
- Confidentiality(기밀성)
- Data Confidentiality: 기밀 정보가 허가되지 않은 개인에게 공개되지 않도록 보장
- Privacy: 개인들이 자신과 관련된 정보를 수집하고 저장할 수 있으며, 누구에게 공개할 수 있는지 통제 가능하도록 보장
- Integrity(무결성)
- Data Integrity: 데이터가 승인된 방식으로만 변경되도록 보장
- System Integrity: 시스템이 무단 조작으로부터 손상되지 않은 방식으로 의도된 기능을 수행하도록 보장
- Availability(가용성): 시스템이 신속하게 작동하고 인증된 사용자에게 서비스가 거부되지 않도록 보장
Additional Security Concepts(AAA)
- Authentication: 사용자 식별
- Authorization: 사용자가 특정 작업을 수행하도록 허용, 사용자에게 어떤 권한이 있는지 확인
- Accounting: 사용자가 액세스하는 동안 사용하는 자원 측정
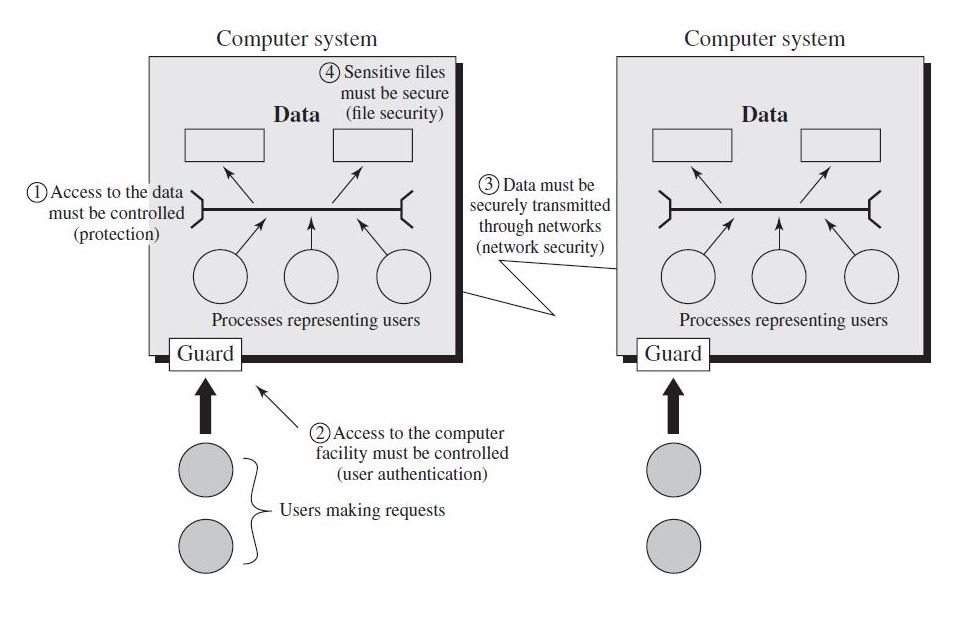
Security Concepts and Relationships
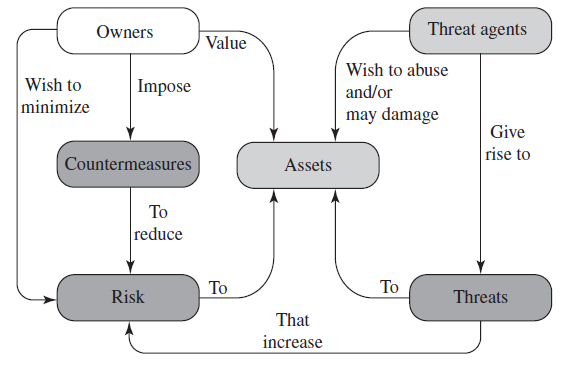
Vulnerabilities, Threats and Attacks
- Categories of Vulnerabilities
- Corrupted(무결성 잃음)
- Leaky(기밀성 잃음)
- Unavailable or very slow(가용성 잃음)
- Threats
- Exploiting vulnerabilites(취약성 이용)
- Potential security harm to an asset
- Attacks
- Passive: 시스템 자원에 영향을 주지 않는다
- Active: 시스템 자원이나 운영에 영향을 준다
- Insider: 내부의 개체에 의해 발생
- Outsider: 외부에 의해 발생
Threat Consequences
- Unauthorized Disclosure(기밀성 위협)
- Exposure
- Interception
- Inference: 간접적으로 sensitive data에 접근하여 추론
- Intrusion: 시스템의 보안을 회피하여 중요한 데이터에 접근, 침입
- Deception(무결성 위협)
- Masquerade: 인증된 entity로 위장하여 악의적인 작업 수행
- Falsification: 위조된 데이터로 속임
- Repudiation: 어떤 행위에 대한 책임을 거짓으로 부인하며 다른 이를 속임
ex) 사용자는 어떤 데이터를 전송한 것을 부인하거나 수신, 소유하는 것을 부인함(실제로는 전송, 수신, 소유 하였음에도)
- Disruption(중단: 가용성, 시스템 무결성 위협)
- Incapacitation: 시스템 가용성에 대한 공격, 트로이 목마, 바이러스 또는 웜과 같은 악성 소프트웨어로 일부 서비스를 비활성화하는 방식으로 작동함
- Corruption: 시스템 무결성에 대한 공격, 기능이나 데이터를 수정하는 방식
- Obstruction: 시스템 작동을 방해하여 전송 등을 중단함
- Usurpation(찬탈: 시스템 무결성 위협)
- Misappropriation: 프로세서 및 운영체제 자원을 무단 사용
- Misuse: 보안 기능을 사용하지 않도록 설정하거나 차단함
Scope of Computer Security
Passive and Active Attacks
- Passive Attacks: 시스템에서 정보를 학습하거나 사용하려고 하지만 시스템 리소스에 영향을 미치지 않는다.
- Eavesdropping(감청), Monitoring transmissions
- Detect하기 힘들다
- Detection보다는 예방에 초점
- Release of message contents / Traffic analysis
- Active Attacks: 데이터 스트림을 일부 수정하거나 거짓 데이터 스트림을 생성한다.
- Detect해서 Recover하는 것이 목적
- Masquerade / Replay / Modification of messages / DoS
Security Functional Requirements
- 기술정 방법이 필요
- Access control
- Identification & Authentication
- System & Communication protection
- System & Information integrity
- 관리 통제 및 절차 필요
- Awareness & Training
- Audit & Accountability
- Certification, Accreditation, Security assessments
- Contingency planning, Maintenance
- Physical & Environmental protection, planning
- Personnel Security
- Risk assessments, Systems & Services acquisition
- 1번, 2번 둘 다 필요
- Configuration management
- Incident response
- Media protection
Security Services
- Authentication Service
- Peer Entity Authentication: 통신하는 상대방의 신원을 확인
- Data-Origin Authentication: 데이터의 출처에 대한 확인(복제 또는 수정에 대한 보호 기능을 제공하진 않음)
- Access Control Service: 통신링크를 통해 호스트 및 애플리케이션에 대한 액세스를 제한하고 제어할 수 있는 기능
- Nonrepudiation Service
- Data Confidentiality Service
- Connection Confidentiality
- Connectionless Confidentiality
- Selective-Field Confidentiality
- Traffic-Flow Confidentiality
- Data Integrity Service
- Availability Service
X.800 Security Mechanisms(Specific vs. Pervasive)
- Specific Security Mechanisms
- Encipherment(암호화)
- Digital Signature(디지털 서명): 수신자가 송신자의 무결성을 입증하고 위조를 막도록 데이터에 붙이는 데이터나 데이터 단위의 암호적 변경을 말한다
- Access Control(접근 제어)
- Data Integrity(데이터 무결성)
- Authentication Exchange(인증 교환): 정보교환을 통해 개체의 신원을 확인
- Traffic Padding(트래픽 패딩): 데이터 스트림 안의 빈곳에 비트를 채워 넣어 트래픽 분석 시도를 방해함
- Routing Control(경로 제어): 물리적으로 안전한 경로를 선택할 수 있게 함
- Notarization(공증): 데이터 교환의 어떤 성질들을 확신하기 위해 신뢰받는 제 3자를 이용함
- Pervasive Security Mechanisms
- Trusted Functionality(신뢰받는 기능)
- Security Label(보안 레이블)
- Event Detection(이벤트 탐지)
- Security Audit Trail(보안 감사 추적): 시스템 기록과 동작을 독립적으로 조사하고 검토
- Security Recovery(보안 복구)
Computer Security Strategy
- Specification / Policy
- Implementation / Mechanisms
- Detection
- Response
- Recovery
- Prevention
- Assurance / Evaluation